බෙන්සීන්
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Benzene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS number | {{{value}}} | ||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:{{{value}}} | ||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.685 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | {{{value}}} | ||
| PubChem | {{{value}}} | ||
| RTECS number | {{{value}}} | ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| InChI | |||
| SMILES | |||
| Properties | |||
| Molecular formula | C6H6 | ||
| Molar mass | 78.11 g mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Odor | Aromatic, gasoline-like | ||
| Density | 0.8765(20) g/cm3[1] | ||
| Melting point |
5.53 °C, 279 K, 42 °F | ||
| Boiling point |
80.1 °C, 353 K, 176 °F | ||
| Solubility in water | 1.53 g/L (0 °C) 1.81 g/L (9 °C) 1.79 g/L (15 °C)[2][3][4] 1.84 g/L (30 °C) 2.26 g/L (61 °C) 3.94 g/L (100 °C) 21.7 g/kg (200 °C, 6.5 MPa) 17.8 g/kg (200 °C, 40 MPa)[5] | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in alcohol, CHCl3, CCl4, diethyl ether, acetone, acetic acid[5] | ||
| Solubility in ethanediol | 5.83 g/100 g (20 °C) 6.61 g/100 g (40 °C) 7.61 g/100 g (60 °C)[5] | ||
| Solubility in ethanol | 20 °C, solution in water: 1.2 mL/L (20% v/v)[7] | ||
| Solubility in acetone | 20 °C, solution in water: 7.69 mL/L (38.46% v/v) 49.4 mL/L (62.5% v/v)[7] | ||
| Solubility in diethylene glycol | 52 g/100 g (20 °C)[5] | ||
| log P | 2.13 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 12.7 kPa (25 °C) 24.4 kPa (40 °C) 181 kPa (100 °C)[6] | ||
| UV-vis (λmax) | 255 nm | ||
| -54.8·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Solubility product, Ksp | 1.5011 (20 °C) 1.4948 (30 °C)[5] | ||
| Viscosity | 0.7528 cP (10 °C) 0.6076 cP (25 °C) 0.4965 cP (40 °C) 0.3075 cP (80 °C) | ||
| Structure | |||
| Molecular shape | Trigonal planar | ||
| 0 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfH |
48.7 kJ/mol | ||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
173.26 J/mol·K[6] | ||
Heat capacity (C)
|
134.8 J/mol·K | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
potential occupational carcinogen, flammable | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  සැකිල්ල:GHS08[8] සැකිල්ල:GHS08[8]
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H225, H304, H315, H319, H340, H350, H372[8] | |||
| P201, P210, P301+P310, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P331[8] | |||
| Flash point | {{{value}}} | ||
| 497.78 °C (928.00 °F; 770.93 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 1.2–7.8% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
930 mg/kg (rat, oral) | ||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
44,000 ppm (rabbit, 30 min) 44,923 ppm (dog) 52,308 ppm (cat) 20,000 ppm (human, 5 min)[10] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1 ppm, ST 5 ppm[9] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
Ca TWA 0.1 ppm ST 1 ppm[9] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
500 ppm[9] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | HMDB | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
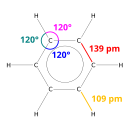
බෙන්සීන් යනු වැදගත් කාබනික රසායනික සංයෝගයකි. එහි රසායනික සූත්රය C6H6 වේ. බෙන්සීන් අණුවක් සමන්විත වන්නේ හයිඩ්රජන් පරමාණු 6ක් එක බැගින් සබැඳුණු කාබන් පරමාණු 6ක් වළල්ලක් සේ හා වීම මඟින් ය. කාබන් හා හයිඩ්රජන් පරමාණුවලින් පමණක් සමන්විත වන නිසා එය හයිඩ්රොකාබනයක් ලෙස වර්ගීකරණය වෙයි. තාපාංකය 80C ද ද්රවාංකය 5C ද ෙ.
බෙන්සීන් ඛනිජ තෙල්හි ස්වභාවික සංඝටකයක් වන අතර මූලික පෙට්රෝරසායනයක් වෙයි. කාබන් පරමාණු අතර චක්රීය නොකැඩි පයි බන්ධනය හෙයින් බෙන්සීන් ඇරෝමැටික හයිඩ්රොකාබනයක් ලෙස [දෙවැනි [n]-ඇන්යූලීනය ([6]-annulene)ලෙස] වර්ග කරයි. යම්විටෙක Ph–H ලෙස ද කෙටි කර ලියයි. බෙන්සීන් සුගන්ධ, අවර්ණ හා අති ගිනිගන්නාසුලු ද්රවයකි. පෙට්රල් පිරවුම්හල් අසල ඇති ගන්ධයට වගකිවයුත්තේ ද එය යි. කිලෝග්රෑම් බිලියන ගණන් නිපදවෙන එතිල්බෙන්සීන් හා ක්යූමීන් වැනි වඩා සංකීර්ණ ව්යූහැති රසායනයන් නිපැයුමේදී පුරෝගාමී රසායනයක් ලෙස සාමාන්යයෙන් බෙන්සීන් භාවිතා වේ. බෙන්සීන්වලට ඉහළ ඔක්ටේන් අංකයක් ඇති නිසා, එය ගැසලීන්හි වැදගත් සංඝටකයකි.
බෙන්සීන් මිනිසුන්ට පිළිකාකාරකයක් නිසා කාර්මික නො වන යෙදුම් සඳහා බෙන්සීන් භාවිතය සීමා වෙයි.
c ප්රතිශතය අධික නිසා දහනයේදි අධික කළු දුමාරයක් පිටවේ.
ව්යූහය
[සංස්කරණය]
නිපදවීම
[සංස්කරණය]කාර්මිකව බෙන්සීන් නිෂ්පාදනය සඳහා රසායනික ක්රියාවලි 4ක් මුල් වෙයි: උත්ප්රේරික පිළිසකරුව, ටොලුයීන් හයිඩ්රෝවිඇල්කිල්කරණය, ටොලුයීන් ද්විධාකරණය හා වාෂ්ප බිඳීම. බෙන්සීන්හි ATSDR විෂවිද්යාත්මක පැතිකඩ අනුව 1978 හා 1981 අතර, ඇ.එ.ජ. බෙන්සීන් නිෂ්පාදනයෙන් 44-50% ප්රමාණයක් උත්ප්රේරිත පිළිසකරුවෙන් නිපදවා ඇත.[11]
යොමු
[සංස්කරණය]- ^ Lide, D. R., ed. (2005), CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (86th ed.), Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press,
- ^ Arnold, D.; Plank, C.; Erickson, E.; Pike, F. (1958). "Solubility of Benzene in Water". Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Chemical & Engineering Data Series. 3 (2): 253–256. doi:10.1021/i460004a016.
- ^ Breslow, R.; Guo, T. (1990). "Surface tension measurements show that chaotropic salting-in denaturants are not just water-structure breakers". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 87 (1): 167–9. Bibcode:1990PNAS...87..167B. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.1.167. PMC 53221. PMID 2153285.
- ^ Coker, A. Kayode; Ludwig, Ernest E. (2007). Ludwig's Applied Process Design for Chemical And Petrochemical Plants. Vol. 1. Elsevier. p. 114. ISBN 0-7506-7766-X. සම්ප්රවේශය 2012-05-31.
- ^ a b c d e සංරක්ෂිත පිටපත, http://chemister.ru/Database/properties-en.php?dbid=1&id=644, ප්රතිෂ්ඨාපනය 2018-05-06
- ^ a b c සැකිල්ල:Nist
- ^ a b Atherton Seidell; William F. Linke (1952). Solubilities of Inorganic and Organic Compounds: A Compilation of Solubility Data from the Periodical Literature. Supplement. Van Nostrand.
- ^ a b c Sigma-Aldrich Co., Benzene. Retrieved on 2014-05-29.
- ^ a b c සැකිල්ල:PGCH
- ^ සැකිල්ල:IDLH
- ^ Hillis O. Folkins (2005). "Benzene". Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. .