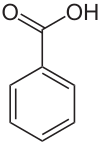
බෙන්සොයික් අම්ලය
Appearance
සැකිල්ල:Chembox DeltaHc
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Benzoic acid[1] | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Benzenecarboxylic acid | |||
| වෙනත් නාම
Carboxybenzene; E210; Dracylic acid; Phenylmethanoic acid
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS number | {{{value}}} | ||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | |||
| 636131 | |||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:{{{value}}} | ||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.562 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| E number | E210 (preservatives) | ||
| 2946 | |||
| KEGG | {{{value}}} | ||
| MeSH | {{{value}}} | ||
| PubChem | {{{value}}} | ||
| RTECS number | {{{value}}} | ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| InChI | |||
| SMILES | |||
| Properties | |||
| Molecular formula | C7H6O2 | ||
| Molar mass | 122.12 g mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless crystalline solid | ||
| Odor | faint, pleasant odor | ||
| Density | 1.2659 g/cm3 (15 °C) 1.0749 g/cm3 (130 °C)[2] | ||
| Melting point |
122 °C, 395 K, 252 °F | ||
| Boiling point |
250 °C, 523 K, 482 °F | ||
| Solubility in water | 1.7 g/L (0 °C) 2.7 g/L (18 °C) 3.44 g/L (25 °C) 5.51 g/L (40 °C) 21.45 g/L (75 °C) 56.31 g/L (100 °C)[2][3] | ||
| Solubility | soluble in acetone, benzene, CCl4, CHCl3, alcohol, ethyl ether, hexane, phenyls, liquid ammonia, acetates | ||
| Solubility in methanol | 30 g/100 g (-18 °C) 32.1 g/100 g (-13 °C) 71.5 g/100 g (23 °C)[2] | ||
| Solubility in ethanol | 25.4 g/100 g (-18 °C) 47.1 g/100 g (15 °C) 52.4 g/100 g (19.2 °C) 55.9 g/100 g (23 °C)[2] | ||
| Solubility in acetone | 54.2 g/100 g (20 °C)[2] | ||
| Solubility in olive oil | 4.22 g/100 g (25 °C)[2] | ||
| Solubility in 1,4-Dioxane | 55.3 g/100 g (25 °C)[2] | ||
| log P | 1.87 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 0.16 Pa (25 °C) 0.19 kPa (100 °C) 22.6 kPa (200 °C)[4] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.202[5] | ||
| -70.28·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Solubility product, Ksp | 1.5397 (20 °C) 1.504 (132 °C)[2] | ||
| Viscosity | 1.26 mPa (130 °C) | ||
| Structure | |||
| Crystal structure | Monoclinic | ||
| Molecular shape | planar | ||
| 1.72 D in Dioxane | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfH |
-385.2 kJ/mol[2] | ||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
167.6 J/mol·K[2] | ||
Heat capacity (C)
|
146.7 J/mol·K[4] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Irritant | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 සැකිල්ල:GHS07[6] සැකිල්ල:GHS07[6]
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H318, H335[6] | |||
| P261, P280, P305+P351+P338[6] | |||
| Flash point | {{{value}}} | ||
| 571 °C (1,060 °F; 844 K)[7] | |||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
1700 mg/kg (rat, oral) | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | JT Baker | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
බෙන්සොයික් අම්ලය, C7H6O2 (හෝ C6H5COOH), යනු අවර්ණ ස්ඵටිකමය ඝනයක් වන අතර සරල ඇරෝමැටික කාබොක්සිලික් අම්ලයකි. බෙන්සොයික් අම්ලය සොබාවයෙන් බොහෝ ශාක වල හට ගනී.[8] බොහෝ ද්විතීයික පරිවෘත්තජයවල ජෛවසංස්ලේෂණයේ දී අතරමැදියක් ලෙස ක්රියා කරයි. බෙන්සොයික් අම්ලවල ලවණ අහර පිරිරැක්මට යොදන අතර එය නෙක් වෙනත් කාබනික ද්රව්යයන්හි කාර්මික සංස්ලේෂණයෙහි වැදගත් පෙරයෙදුමක් වෙයි. බෙන්සොයික් අම්ලවල ලවණ හා එස්ටර බෙන්සොඒට ලෙස හඳුන්වනු ලැබෙයි.
යොමු
[සංස්කරණය]- ^ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 745. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j උපුටාදැක්වීම් දෝෂය: අනීතික
<ref>ටැගය;chemisterනමැති ආශ්රේයන් සඳහා කිසිදු පෙළක් සපයා නොතිබුණි - ^ Seidell, Atherton; Linke, William F. (1952). Solubilities of Inorganic and Organic Compounds. Van Nostrand. සම්ප්රවේශය 2014-05-29.
- ^ a b c සැකිල්ල:Nist
- ^ Harris, Daniel (2010). Quantitative Chemical Analysis (8 ed.). New York: W. H. Freeman and Company. pp. AP12. ISBN 9781429254366.
- ^ a b c Sigma-Aldrich Co., Benzoic acid. Retrieved on 2014-05-23.
- ^ a b උපුටාදැක්වීම් දෝෂය: අනීතික
<ref>ටැගය;GESTISනමැති ආශ්රේයන් සඳහා කිසිදු පෙළක් සපයා නොතිබුණි - ^ "Scientists uncover last steps for benzoic acid creation in plants". Purdue Agriculture News.
බාහිර දිගු
[සංස්කරණය]- ජාක්යන්තර රසායනික ආරක්ෂණ පත්රිකාව 0103
- සැකිල්ල:SIDSOrganisation for Economic Co-operation and Developmentසැකිල්ල:SIDS
- ChemicalLand